Income tax e-filing of Income from other sources is vital. This may be tax free and include investments, selling of property etc. Learn how to declare such income in ITR-1
For the latest income tax rules on new tax regime, visit New Income Tax Regime 2020 and Its Effect on Payroll Processing
Indian Income Tax Department has extended the date of income tax e-filing from July 31st to August 31st. This post has useful information that would help you file ITR-1 and report taxes and investments accurately under “Income from Other Sources” section.
Income Tax Return e-Filing FY 18-19
Income tax refers to indirect and direct taxes. The tax that is deducted directly from one’s personal salary (tax deducted at source by an employer, TDS) is said to be Direct Tax and the tax that is indirectly paid to the government (for example service tax at a restaurant, custom duty, entertainment tax, etc.) is said to be Indirect Tax.
According to Indian Income Tax Department, there are 5 types of income heads that should be carefully filed in the income tax return (ITR): Salary, Capital Gains, House Property, Business/ Professional and Income from Other Sources. Income which is not covered in any of the other heads of income is called Income from other sources.
Income under this head is not taxable, yet it is important to declare it in ITR e-filing
For e-filing of FY 2018-19, tax experts even suggest declaring interest from PPF and bonds at the time of maturity under schedule EI (Exempt Income).
Report Income from Other Resources in ITR-1
This year’s filing details under “Income from Other Sources” is different from that of last year. If you don’t include income from other sources in the ITR, the income tax department may consider it a case of tax evasion. The department can even send a notice to the defaulter seeking explanation for not mentioning income from other sources in their tax return.
In the ITR form, 5 types of income received by an individual are considered as Income from Other Sources. These options are:
- Interest from Savings Account
- Interest from Deposit (Bank/Post office/Co-operative society)
- Interest from Income Tax Refund
- Family Pension
- Any other
Interest from Savings Account
Banks do not deduct TDS on Interest generated on savings account, but information of interest collected in savings account and post office deposits must be declared in the tax return filing. Enter the total amount of interest received by you from all your bank and post office deposit accounts. Interest from Recurring Deposit (RD) and Fixed Deposits (FD) is taxable, and these can be identified from the savings account interest entries in your passbook.
Interest from Deposit (Bank/Post office/Co-operative society)
An individual’s investment in FD, RD or any scheme like Post Office Time Deposit (POTD) and Senior Citizen Savings Account (SCSS) needs to be declared in ITR-1. Mention the total interest received from various deposits in FY 2018-19.
Interest from Income Tax Refund
As per the Income Tax Act, the tax refund received by an individual is not taxable. However, the interest received on tax refund becomes taxable. The interest on income tax refund is paid by the department if the refund amount is more than 10 percent of the tax paid. The interest amount can be verified in Form 26AS as it shows tax refund and interest on it separately.
Family Pension
Pension collected on behalf of a deceased person is mentioned under “Income from Other Sources”. Either Rs. 15,000 or 1/3rd of the family pension (which ever is low) is deducted under the Family Pension Income. This amount gets added with the taxpayer’s income and tax is paid at the applicable interest rate.
Any Other
Any other income received from above mentioned sources is taxable and mentioning their details in ITR-1 is mandatory. Other incomes that are taxable under “Income from Other Sources” are company fixed deposits, sovereign gold bonds and more.
A person is liable to pay Gift Tax, if he/ she receives gifts (either in cash or kind). Such income is taxable under the head “Income from other sources”. Tax computation for gifts depends upon its value and the occasion when it has been gifted.
- (i) Gifts received from relatives are fully exempted from the tax.
- (ii) Gifts received by a person on his own wedding are completely exempted from tax.
- (iii) If the total gift value received from people is less than INR 50,000 in a financial year, it is not liable for Gift Tax. When exceeding gift value of INR 50,000, then the entire gift amount is taxable.
- (iv) Gifts received as a movable asset, the fair market value would be considered to pay tax and for an immovable asset, the stamp duty is considered.
- (v) Gift received from a Will or Inheritance or in contemplation of death is completely tax free and there is no maximum limit in such cases.
Who should file ITR-1?
ITR-1 SAHAJ form is filed by Individuals whose income is within ₹ 50 Lakhs. Their source of income can be from Salary or Pension, from only one House Property and from other sources excluding lottery, racehorses, legal gambling etc.
If you have income from foreign assets, agricultural income that exceeds Rs. 5000, income from business or profession and income from more than one house property then you are not eligible to file ITR-1.
How does a Payroll Software help in income tax return e-filing?
Employers use online payroll software to deduct taxes from employee salaries and remain statutory compliant. The use of an automated payroll software makes the process quick, accurate and efficient. Some of the well-designed software, like Empxtrack, even allow employees to declare their income from other sources. The image below describes the various heads under which income from other sources can be mentioned.
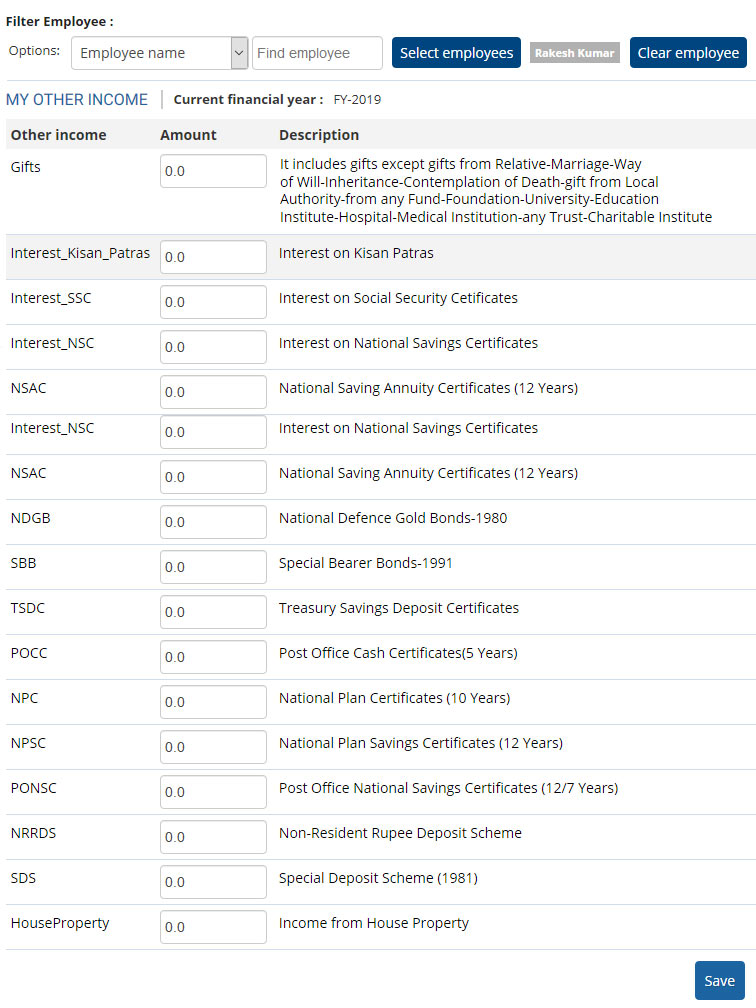
When Form 16 is generated automatically from the payroll system, total income of an employee is reflected in it. The system records income details of all sources earned throughout a financial year and calculates and deducts the taxes accordingly.
For instance, an employee’s income is Rs 10 lakh per annum, and they receive a gift of rupees 2 lakh in the same financial year. Then total taxable income would be Rs 12 lakh per annum and the tax deductions will be made according to income tax rules. By declaring income from other sources in Empxtrack payroll, an employee skips the hassle of generating challans from the bank which is a tedious and time-consuming task.
Remember, even though income from other sources in non-taxable, yet it is important to declare it in ITR e-filing.
Process payroll for 25 employees at no cost
* No credit card required








This is such a nice blog on the income filing of income from other sources. This article is one of the beautiful article which attracts me a lot. I enjoyed a lot while reading this article and would suggest others too and get the best options.for more info.
I read your blog. It’s very nice and very useful for me. Thanks for sharing useful information with us. I’m India Tax and we provide Taxation, Income Tax Return, Assurance, Consulting, Mergers and Acquisition to Corporate Financial Advisory and also provide franchise for more information Visit our website itaxinfo
Very informative and detailed article
I found your article very informative and I totally love how the concepts are explained in this blog post. Thanks for sharing your insights. It helps a lot.