This blog explains the steps involved in Payroll calculations to minimize challenges and develop a satisfied workforce.
6% – 13% employees have payroll related challenges every pay period. Most of these lead to queries for the payroll processing department (HR or accounts) and create significant dissatisfaction, re-work, stress and disruptions.
It is believed that a payroll processing software can help avoid these challenges. Yes, this is true but only partly!
A good payroll software helps but only so much. A well-defined and streamlined payroll process with a suitable payroll software can help you completely avoid disruptions, cut costs and increase employee satisfaction.
Initial considerations for Payroll Calculations
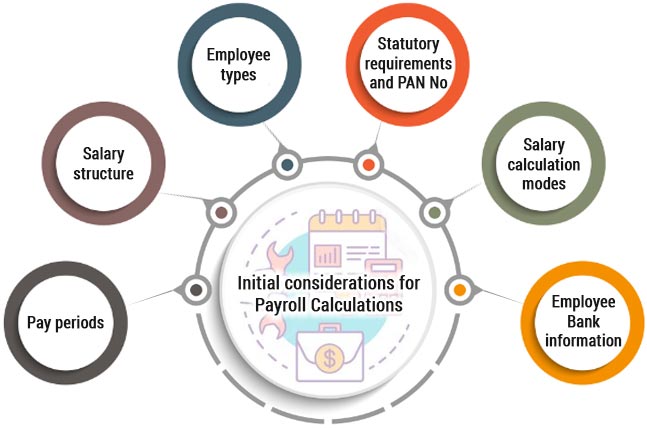
Pay periods
Pay periods are the dates for which payroll calculations are carried out and span a month, a fortnight or a week. Monthly payouts are most common.
A payroll is calculated at the end of each pay-period. There are a few important considerations while defining pay periods.
- All government reporting related to payroll corresponds to financial years and is broken down into monthly, quarterly, half-yearly and annual returns of different types.
- To ease and streamline the processes, the pay periods should ideally correspond to the financial year. In the Indian payroll context financial years span 01 Apr to 31st March of the following year. Your pay periods should map to this as well.
- There should be a gap of 3 – 5 days between the end of the pay period and the payout date. This reduces pressure on the payroll processing department. So if you want to pay salary on the 1st of each month, the corresponding pay period should end on the 25th of the prior month.
Salary structure
There may be different types of employees in your organization and it is helpful to define one or more salary structure for each type of employee.
The salary structure is a collection of salary heads that include
- – Wages (Basic salary),
- – Allowances (Dearness Allowance, House Rent Allowance, Transportation Allowance etc.),
- – Benefits (Retirement benefits: Provident Fund & Gratuity, Health Insurance: ESI, Medical Insurance) and
- – Accruals (Annual Bonus, Performance Linked Bonus)
- – Claims (Tax free allowances to employees against bills. Include Book allowance, Telephone allowance, Driver allowance, Petrol allowance)
- – Perquisites (These are not paid to employees but included in their salary structures and taxable)
Miscellaneous heads are not included in salary structures and include Rewards, Referral bonus, Joining bonus, Sales Commissions and expense reimbursements.
A salary structure helps in easy identification of CTC (Cost to Company ), running reports, creating offer letters and managing increments and helps in streamlining the payroll process.
Remember that a salary structure is just a template that contains various heads. The values for each salary head will vary for each employee.
Employee types
There are different salary components and taxation rules for different kinds of employees. You need to identify the employee types applicable to your company.
While the topic is a blog in itself, the different kinds of employees covered include: Salaried, Hourly, Piece rate, Consultants and Commission agents. This blog post applies to the first two categories viz Salaried and Hourly employees.
Statutory requirements and PAN No
For Salaried and Hourly employees, there are a number of statutory obligations that include
- – Minimum wages (based on the location of work of the employee)
- – Provident Fund (largely universal and based on your companys’ size)
- – Health Insurance (ESI) (based on the availability of ESI clinics / hospitals and your companys’ size)
- – Professional Taxes (based on the state where the employee works)
- – Statutory Bonus (based on the state where the employee works) and
- – Gratuity (largely universal and based on your companys’ size)
Government of India has mandated that the employer record PAN No of every employee whose payroll is getting calculated, especially where taxes are deducted. This PAN number is required as a part of many different reports that have to be submitted as a part of statutory filing. There are additional such identifiers including PF No, ESI No that transfer the benefit deductions to the correct employee records.
Salary calculation modes
Indian tax structure is fairly complicated with various deductions and exemptions.
Accurate deductions (taxes and benefits) are the responsibility of the employer, hence it is important to define the basis of the salary calculation, document it, and share it with all employees. You can include this in your company policy document.
Most companies use Leave Without Pay (absent without leave) or Days worked to calculate the eligible salary.
Besides a base salary, additional payouts mechanisms may include pieces created (piece rate employee), sales achieved (commission based employee).
Employee Bank information
Salary payment by cash has logistic challenges and is being discouraged by the government. Check payments often take longer to transfer to employees bank account and are inconvenient.
Automatic bank transfers are the new norm for salary payments. Once setup, bank transfer is easier, faster and has a significantly lower cost.
Since employees may maintain an account in a bank that is different from the companys’ bank account, it is important to maintain bank transfer information for each employee.
Salary Calculation Preparation
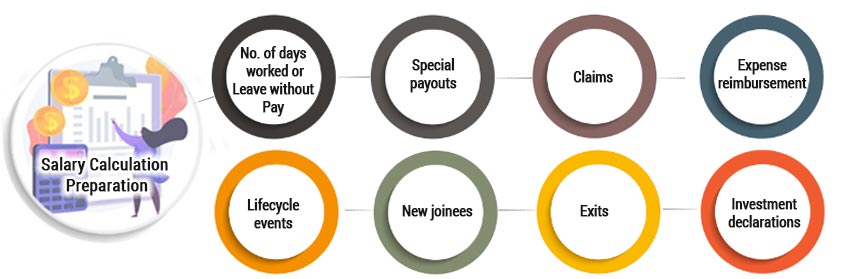
Before you pay the salary, there are a number of steps that need to be carried out for accurate salary calculation.
Identification of Number of days worked or Leave without Pay
This step is often the most time consuming and prone to errors. Employees may have been marked absent (leave without pay) while they were on a business meeting, client visit or they applied for leave but it was not approved by their manager.
In other cases, employees may have not regularized their attendance, overtime hours or compensatory off was not recorded or approved.
Each of these situations leads to incorrect calculation of the salary payout and is the primary reason for payroll calculation related challenges, errors, rework and dissatisfaction.
HR needs to run reports and identify any such situations preemptively. Employees or managers need to be contacted and errors rectified.
A self services platform that includes Attendance and Leave can assist HR significantly in this area.
Special payouts
Employees are sometimes paid outside the payroll and this includes special rewards and recognitions, sales commissions, referral bonuses and so on. These are often done by senior management, owners, BU heads and HR or accounts does not get involved in the payout.
While this practice encourages the correct behavior, the key challenge is in recording these payments and ensuring that appropriate taxes are deducted. Follow these rules to avoid audit related challenges
- – Institute a process that encourages a reward to be given as a letter and not a check.
- – Ensure that HR is always intimated when such a reward or recognition is given.
- – If the payout is to be made prior to the payroll, ensure that appropriate taxes are deducted. Unless the amounts are very small, ensure that the payment is by check.
- – Include this payout as payments outside the payroll prior to the payroll calculation.
Note: Empxtrack offers a feature Capture payments outside the payroll to handle this situation and Empxtrack accurately calculates taxes to keep you statutorily compliant.
Claims
Senior employees may be offered certain tax free benefits based on their job requirements. These include reimbursements of various types such as mobile reimbursement, car maintenance allowance, driver salary, petrol allowance, meal & entertainment allowances.
While the last item is not a part of the salary structure, others may be included to reduce the tax outgo of the employee.
You need to collect the claimed amount for each eligible employee, tally it with eligibility, validate the bills submitted and payout the same as a non-taxable or taxable amount.
If you have a large employee base using such benefits, a workflow driven self-services platform would help manage this better. In any case, any such amounts will need to be recorded prior to the payroll run.
Expense reimbursement
Often expenses are reimbursed in the payroll. In case your company follows this process too, it is important to get all such expense reports – duly approved from the managers and included in the payroll prior to the calculation.
Lifecycle events
There could be a number of different lifecycle events and these may impact salary calculations and deductions. These include
- – Addition and removal of dependents (impact on taxes and benefit costs)
- – Addresses changes (impact on taxes)
- – Investment changes (such as house loan or payback)
- – Election of new benefits (impact on benefit costs and taxes)
- – Promotions, salary increments and salary structure changes (impact on arrears, taxes)
Each of these events needs to be identified and communicated for accurate salary calculations.
New joinees
A new joinee needs to be added to the HRIS with all data records (such as PAN No, address information, dependent information), salary structure and benefit deductions.
To allow accurate calculation of taxes, you also need to capture prior salary information through Form 12B.
To ensure that payroll calculations for new joinees is accurate and does not disrupt the process for all other employees, identify a cut-off date post which you will not include the new joinee in the current months’ payroll.
As an example, if your pay period is from 26th through 25th of next month, exclude all new joinings after 20th in the current payroll run. The new joinee would have additional days counted in the subsequent pay-period. Communicate this to the new joinee as also make this a part of your company policy.
Exits
Many companies stop the payroll run for employees who have handed in their resignations. This is tricky – especially in cases where employees just stop coming to work post the pay period end date (eg. absconding employees). But can be achieved if we separate the payroll processing and disburse processes.
In case you have a formal clearance and Full and Final process, try to keep it after the payroll payout date to reduce the workload.
Educate your managers to communicate immediately if they receive a resignation or believe that they have an absconding employee.
An exit process that ties into your payroll can reduce workload in managing exited employees.
Investment declarations
Indian payroll allows various deductions under sections such as 80C, 80D, 24B. Employees declare their investment plans under these schemes at the beginning of the year. House rent is also declared by employees.
This allows a reduced tax outgo.
To ensure accurate taxes towards the end of the financial year, you need to collect proof of the declarations and then change values as required. This should be done in a timely manner and it is recommended that you identify a pay-period, say Oct, where you will deduct taxes based on actual investments made by employees. For the period Jan – Mar, you in-any-case need to use actual investments as a basis of tax calculation.
Salary calculation process
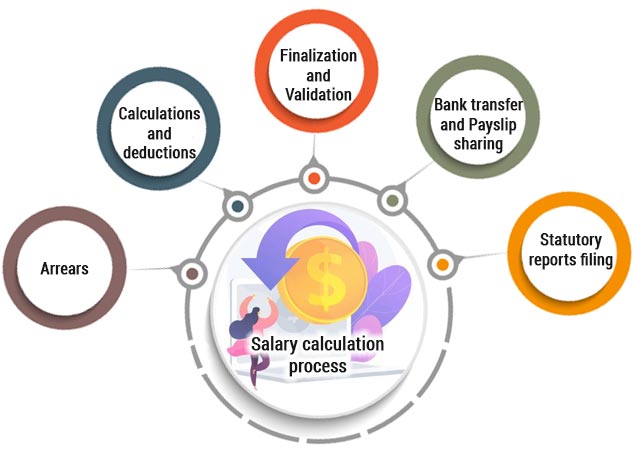
Once you have identified all the areas that impact salary calculations and collected all the data points, now it is time to calculate the gross salary, deductions and net salary. There are a few things to consider here too.
Arrears
An employees’ salary may have changed in a prior period because there was a delay in the performance increment cycle.
The salary changes will need to be paid retrospectively and this calculation is called Arrear calculation. The calculation will include additional income, increased taxes and deductions.
Once you have identified such cases, include the additional salary and deductions in the payroll run.
Calculations and deductions
Once you have identified all the elements for payroll calculations, it is easy to calculate the gross salary and deductions. Prior to calculations, a gap report can be created to identify any suspected challenges – such as missing attendance, lack of availability of PAN number, address change and so on. This report can preempt the removal of errors.
While the below calculations may not cover all cases, it can help you plan the calculations
| Illustrative calculation | Comments | |
|---|---|---|
| Eligible Monthly Salary | Monthly Salary * (Total days in Month – Leave without Pay) / total days in month |
Formula can vary based on the calculation basis. We can have hours worked, a piece rate, overtime, or fixed amount to identify the Eligible Monthly Salary. |
| Gross taxable Payout | Eligible Monthly Salary + Taxable Claims + Arrears + Payments outside payroll | |
| Taxes | Taxes on Gross taxable Payout |
Taxes calculation is complex since we have to identify total yearly taxes by reducing yearly income by exemptions and deductions, reduce the amount of taxes paid already and divide the remaining amount by the pending pay periods Taxes will be different for consultants and commission agents. |
| Other deductions | ESI PF Gratuity Professional Taxes Others Health insurance | Rates as applicable |
| Net Payout | Gross taxable Payout + Non-taxable Claims – Taxes – Other deductions |
This is the salary transferred to the bank. |
Finalization and Validation
It is always better to introduce a maker-checker process in your payroll. The maker does all of the above activities and the checker (who can be a senior employee such as CFO, Head HR or company director) who approves the processing.
The best way to validate a payroll is to compare it against a prior months payroll. Dig deeper to identify reasons for any changes and you will be quickly done with approvals.
Bank transfer and Payslip sharing
Post finalization, the payroll can be marked disbursed on the payout date. Additionally, salary slips can be printed and shared by email or enabled on the self-services portal.
Bank reports are created to allow electronic transfers from your companys’ account to individual accounts.
Statutory reports filing
There are a number of reports that are required post payroll processing and each of these follows its own cycle. More information is available on the blog Statutory Compliances in Indian Payroll Management System but at a high level, the reports include
| Period | Payroll reports and challans |
|---|---|
|
Monthly | Provident Fund ESI Professional Taxes TDS |
|
Quarterly | Form 24Q |
| Annual | Form 16 Form 24 Q (last quarter 24Q is annual) |
Conclusion
Timely payroll processing is a difficult and challenging process but if the above steps are communicated and followed diligently, the work of your payroll processing team can reduce significantly.
Implementing a payroll process that handles payroll calculations in a predictive manner with zero errors indicates a mature and stable company and leads to higher satisfaction amongst employees and HR.
Process payroll for 25 employees at no cost
* No credit card required








Just discovered this Future Salary Calculator, and I’m blown away by its features. It’s intuitive, comprehensive, and perfect for anyone looking to plan their financial future confidently.
This is a very nice one and gives in-depth information. I am really happy with the quality and presentation of the article. I’d really like to help appreciate it with the efforts you get with writing this post. Thanks for sharing
Thanks for pointing out that when there is a change in an employee’s benefits, it should also be reflected in their payroll. I’m thinking about hiring an entire kitchen staff for my restaurant business that will open next year and this will be the first time in my life that I will be having employees. Perhaps it would be better if I just get some payroll processing services so that it can be managed properly and with little chance for errors.